This page covers a non-latest version of Handsontable.
# Migrating from 7.4 to 8.0
- Overview
- Context
- General guidelines
- Keywords (alphabetically)
- Installation
- Breaking changes of 8.0.0
- Removals of hooks
- Removing redundant render() from after* hooks
- Plugins no longer enable other plugins
- Data reference and ObserveChanges plugin
- Changes in ManualRowMove and ManualColumnMove plugins behavior
- Changes in ManualColumnFreeze plugin behavior
- Using minSpareRows option with TrimRows plugin
- Custom editors
- Indexes that exceed the data length
- RecordTranslator in plugins
- Selecting data
- Load data hooks arguments order
- Column and row resizing hooks arguments order
- Selection range have negative indexes
- Removals
# Overview
The purpose of the following guide is to facilitate a smoother update to the 8.0.0 version of Handsontable. We strongly recommend an upgrade to make use of all beneficial changes and fixes brought by the introduction of the completely new architecture for row and column management.
# Context
In prior versions of the Handsontable component, the calculation between physical and visual indexes was based on callbacks between hooks. With time, when the component got more feature, it slowly led to inconsistencies and the calculation was imperfect in some cases due to growing complexity. To fix that there was a major change in the whole system of mapping the indexes. This version introduces index mapper that stores, manages, and registers the indexes globally. Under the hood, it is indirectly responsible for managing both rows and columns, as a single source of truth to refer to. This modification is a major rewrite of the core feature and may result in breaking changes in your application.
# General guidelines
- Check if you use any of the features listed in the Keywords section, you need to address them first after the installation.
- Be sure to test the proposed solutions for keeping backward compatibility, if you experience any problems do not hesitate to reach out to us.
- You can also check the release notes for a complete list of all changes.
# Keywords (alphabetically)
afterFilterafterLoadDataafterRowMoveafterUnmergeCellsbatch()beforeRowMoveCollapsibleColumnsColumnSorting- Data binding
dragColumns()dragRowsFiltersfinalIndexGanttChartHiddenColumnsinsertisMovePossibleManualColumnFreezeManualColumnMoveManualRowMoveminRowsminSpareRowsmodifyColmodifyRowmoveColumnsmoveRowsNestedRowsObserveChangespopulateFromArray()RecordTranslatorsetDataAtCell()setDataAtRowProp()skipLengthCachetoPhysicalColumn()toPhysicalRow()toVisualColumn()toVisualRow()TrimRowsunmodifyColunmodifyRow
# Installation
Use the following command to update the Handsontable to 8th version:
npm install handsontable@8
# Using with wrappers
When you use the wrapper you need to update it as well. Run the following command, respectively:
If you use Handsontable with React:
npm install handsontable@8 @handsontable/react@4
If you use Handsontable with Vue:
npm install handsontable @handsontable/vue@5
If you use Handsontable with Angular:
npm install handsontable@8 @handsontable/angular@6
# Breaking changes of 8.0.0
# Removals of hooks
Hooks related to the visual and physical indexes were removed since new architecture for indexes management was introduced. To achieve the same functionality we suggest using the API. What is more, internal calls in the component's code to these hooks were removed and replaced with corresponding API methods. The following examples show how to preserve previous functionality.
# modifyRow, unmodifyRow, modifyCol, unmodifyCol
modify* and unmodify* hooks for rows and columns were removed. The actions to be taken are similar for both rows and columns.
For example, we will cover modifyRow hook. Prior 8.0.0 to move a row you had to use it
modifyRow(row) {
if (row === 0) {
return 1;
}
if (row === 1) {
return 0;
}
}
In 8.0.0 it is no longer the case. To achieve the same functionality you need to use rowIndexMapper():
hotInstance.rowIndexMapper.moveIndexes([1, 0], 0);
hotInstance.render()
Take look on the trimming example, too. It used to work like this:
data: Handsontable.helper.createSpreadsheetData(10, 10),
modifyRow(row) {
// Trimming first row.
if (row < 9) {
return row + 1;
}
return null;
}
Now, if you want to get the same results you need to use the TrimmingMap:
import { TrimmingMap } from "handsontable/es/translations";
...
const customTrimmingMap = new TrimmingMap();
hotInstance.rowIndexMapper.registerMap('customTrimmingMap', customTrimmingMap);
customTrimmingMap.setValueAtIndex(0, true); // trimming index 0
hotInstance.render();
# hiddenRow, hiddenColumn
If you used HiddenRows or HiddenColumns in your application you need do an update and use a corresponding index mapper:
Prior 8.0.0:
hot.hasHook('hiddenColumn') && hot.runHooks('hiddenColumn', visualColumn);
Now:
hot.columnIndexMapper.isHidden(hot.toPhysicalColumn(visualColumn));
An example for rows:
Prior 8.0.0:
hot.hasHook('hiddenRow') && hot.runHooks('hiddenRow', visualRow);
Now
hot.rowIndexMapper.isHidden(hot.toPhysicalRow(visualRow));
# Removing redundant render() from after* hooks
The sequence of after... hooks changed, for example: afterLoadData, afterFilter, afterUnmergeCells are now called before the render. In the previous versions, you had to call render() to apply changes made with after... hooks. In some cases, depending on the number of hooks registered, it led to rendering all the cells multiple times. Many of these operations were redundant and unnecessary, resulting only in a performance bottleneck.
From now on, you can alter the Handsontable instance in each hook and it will re-render only once. To benefit from this change you have to review all your hooks and remove unnecessary render calls. Example:
instance.addHook('afterFilter', function () {
// ... your operations
instance.render(); // <= remove this line!
});
# Plugins no longer enable other plugins
From version 8.0.0 you can set plugins separately. They no longer rely on each other tightly in terms of functionality, so it is up to the developer to use them simultaneously when needed. You can avoid unwanted "extra" functionality switched on by a supporting plugin.
NestedRows and Filters no longer depend on nor enable TrimRows plugin. To keep using the TrimRows functionality, mostly use API or if your custom plugin is based on it, you need to enable the plugin explicitly:
Before 8.0.0
nestedRows: true
filters: true
After:
nestedRows: true,
trimRows: true
filters: true,
trimRows: true
ManualColumnFreeze does not rely on the ManualColumnMove plugin. To preserve the same functionality as before you need to set it explicitly:
Before 8.0.0
manualColumnFreeze: true
After:
manualColumnFreeze: true,
manualColumnMove: true
ColumnSorting will not enable ObserveChanges. To preserve the same functionality as before you need to set it explicitly:
Before 8.0.0
columnSorting: true
After:
columnSorting: true,
observeChanges: true
CollapsibleColumns plugin no longer uses HiddenColumns plugin, hence it will not be enabled. What's more, it won't enforce the inclusion of the second plugin anymore. To preserve the functionality of hiding columns separately (out of collapsing) as before you need to set it explicitly:
Before 8.0.0
collapsibleColumns: true
After:
collapsibleColumns: true,
hiddenColumns: true
# Data reference and ObserveChanges plugin
Modifying the table’s data by reference and calling render() is no longer feasible. Now all the data-related operations need to be performed using the API methods such as populateFromArray() or setDataAtCell().
The source data API was changed as well and it will no longer return a reference to the source data object. Instead, it returns a copy of the data, possibly already modified by the modifySourceData and modifyRowData hooks. The change applies to all "getter" source methods - getSourceData(), getSourceDataAtCell(), getSourceDataAtRow(), getSourceDataAtCol() and getSourceDataArray().
Since it breaks the link to original data source reference, setSourceDataAtCell() method and afterSetSourceDataAtCell hook were introduced to maintain a similar functionality.
Before it was possible to set source data by reference to the data variable:
data[0][0] = 'A1';
or by getting the reference to the underlying source data:
hotInstance.getSourceData()[0][0] = 'A1';
Now API should be used:
hotInstance.setSourceDataAtCell(0, 0, 'A1');
It is also worth to mention that getSourceData() will return a clone of the entire dataset, when run without arguments - getSourceData(). However, if a row/column range is provided: getSourceData(0, 0, 10, 10), it will filter the dataset with the columns and/or dataSchema options, and return only the columns configured to be visible.
Before it was also possible to extend the row-object by setDataAtRowProp() method when working with an array of objects as source data. Since 8.0.0 the only way to do that is to use setSourceDataAtCell().
Check the following example:
const hot = new Handsontable(container, {
data: [
{ model: 'Roadster', company: 'Tesla' },
{ model: 'i3', company: 'BMW' },
],
});
hot.setDataAtRowProp(0, 'available', true) // This usage will throw an error in 8.0.0.
hot.setSourceDataAtCell(0, 'available', true) // This usage will set a new property in 8.0.0`
# Changes in ManualRowMove and ManualColumnMove plugins behavior
Both plugins has been adapted to work with Index Mappers.
Hooks, beforeRowMove, afterRowMove, beforeColumnMove, and afterColumnMove have different set of parameters now.
Methods moveColumn, moveColumns, moveRow, and moveRows have their arguments changed. From this version onward, the target argument was changed to finalIndex argument. They work differently now and a new dragRow, dragRows, dragColumn and dragColumns methods overtook old methods place in terms of functionality. To put it bluntly, if you want to preserve previous functionality of moveRows rename it to the dragRows.
Important note! If NestedRows is set to enabled the move is possible only by the drag in the UI or dragRow/dragRows methods of the ManualRowMove plugin.
The "drag" methods comes with the dropIndex parameter. It directs where to place the dragged elements. The place you intend to drag the element is managed by drop indexes. You can imagine some sort of a drop zone between actual indexes of elements:
The "move" methods comes with the finalIndex parameter. It tells where to overlap the first element from the moved ones. The place you intend to move the element is managed by visual indexes.
Please note that in case of "move" methods some move actions are limited. For example, if you initiate a move of more than one element to the last position (visual index = the number of items - 1) the operation will be canceled. The first element in the collection you would like to move will try to reach the last position (finalIndex) which is feasible. However, the next ones will attempt to reach the position exceeding the number of all items.
You can find the plugin's isMovePossible API method useful when you want to determine if the move action is possible. movePossible parameter of beforeRowMove, afterRowMove, beforeColumnMove, and afterColumnMove hooks may be helpful as well.
# Changes in ManualColumnFreeze plugin behavior
The ManualColumnFreeze plugin itself also works differently. Before the v8.0.0 frozen columns attempted to go back to original positions upon the unfreeze. Currently, the original position is not calculated. It unfreezes the column just after the "line of freeze". The functionality changed because after several actions like moving the former position was rather estimated than determined.
# Using minSpareRows option with TrimRows plugin
Another breaking change is related to minSpareRows and minRows. The difference is visible when the data is being trimmed (i.e. by the TrimRows plugin) and the options are set. In previous versions the data which was supposed to be trimmed included minSpareRows and minRows which resulted in trimming them along with other rows. In version 8.0.0 spare rows are always present and cannot be removed by trimming.
Check the following code example:
const hotInstance = new Handsontable(container, {
data: Handsontable.helper.createSpreadsheetData(5, 5),
minSpareRows: 2,
trimRows: [1, 2, 3, 4]
});
The results before:
The results after:
To ensure your application works as expected you should review it and search the use cases of minSpareRows or minRows, if the application relied on this mechanism you may need to adapt it. For example, in prior versions the following code:
const hotInstance = new Handsontable(container, {
data: Handsontable.helper.createSpreadsheetData(10, 10),
trimRows: [0],
minSpareRows: 2
}
rendered 0 spare rows. If you want to keep it that way you may need a workaround, for instance:
const hotInstance = new Handsontable(container, {
data: Handsontable.helper.createSpreadsheetData(10, 10),
trimRows: [0],
beforeCreateRow(index, amount, source) {
const rowIndexMapper = this.rowIndexMapper;
// If any row was skipped then block a creation of row execution.
if (source === 'auto' && rowIndexMapper.getNotSkippedIndexesLength() < rowIndexMapper.getNumberOfIndexes()) {
return false;
}
},
minSpareRows: 2
});
# Custom editors
Custom editors will now use data attribute to recognize the input as an editor. Before this change, Handsontable depended on the CSS className. And it had to be handsontableInput. Now it is an attribute - data-hot-input. Focusable and editable elements must have this attribute set up to work properly. ClassNames were freed from restrictive names.
An example with data-hot-input in Custom editor, to make it work properly on a focusable element:
createElements() {
...
this.TEXTAREA.className = 'handsontableInput';
...
}
After the changes:
createElements() {
...
this.TEXTAREA.className = 'anythingYouWant';
this.TEXTAREA.setAttribute('data-hot-input', true);
...
}
# Indexes that exceed the data length
Also, the methods toVisualRow(), toVisualColumn() and toPhysicalRow(), toPhysicalColumn() used to return index numbers that exceeded the overall length. For example:
// Data set with just 10 rows.
const physicalRow = hotInstance.toPhysicalRow(20);
// physicalRow === 20
From now on, if you want to refer to them you will receive null:
// Data set with just 10 rows.
const physicalRow = hotInstance.toPhysicalRow(20);
// physicalRow === null
It can be a breaking change for your project if any parts of it expected the output to be a number, now it will be null. In case you still want to use it as before you need to, for example, check for null and fallback to visual row index:
const visualRow = 20;
const physicalRow = hotInstance.toPhysicalRow(visualRow) ?? visualRow;
// physicalRow === 20
# RecordTranslator in plugins
The RecordTranslator object was removed, as a consequence, t property is no longer available in the plugins. This alias could be used to translate between visual and physical indexes with four methods: t.toVisualRow, t.toPhysicalRow, t.toVisualColumn, t.toPhysicalColumn. It is advised to call the following methods directly on the instance: hotInstance.toVisualRow, hotInstance.toPhysicalRow, hotInstance.toVisualColumn, hotInstance.toPhysicalColumn. The mappers can be accessed using hotInstance.rowIndexMapper and hotInstance.columnIndexMapper properties.
This example shows how to migrate plugins from using t property to calling the method directly on the instance:
Before:
const physicalColumn = this.t.toPhysicalColumn(column);
After the change:
const physicalColumn = this.hot.toPhysicalColumn(column);
# Selecting data
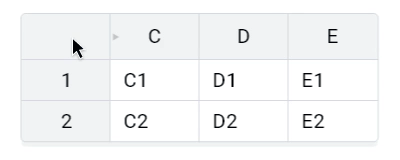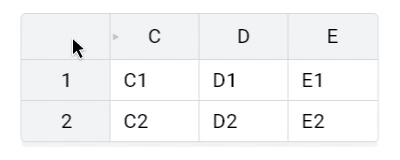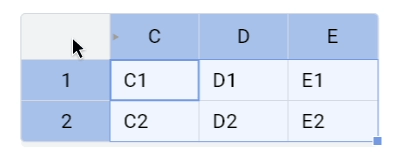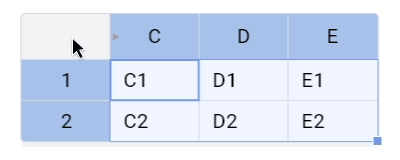
Left mouse button click on the corner will select all cells with headers in 8.0.0.
It used to select just one cell:
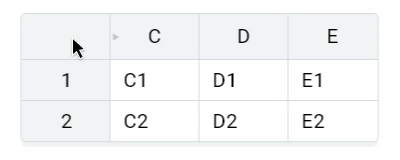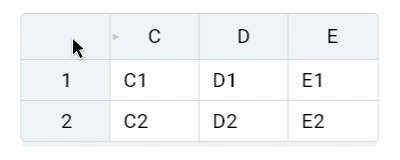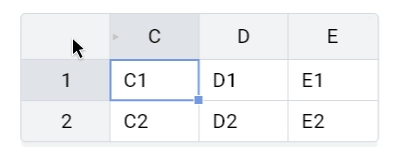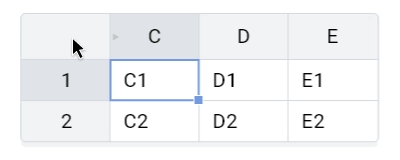
Now the expected behavior is to select all cells:
To keep the previous behavior you need to use the following workaround:
// manipulate the event that happens before the click on cells
beforeOnCellMouseDown(event, coords) {
// apply only for coordinates that are top left corner outside the grid
if (coords.col === -1 && coords.row === -1) {
// stop other event listeners of the same event from being called
event.stopImmediatePropagation();
// use the index mapper method - getVisualFromRenderableIndex on both row and column to choose visual indexes
// this will result in selecting the first cell in the corner
const visualRow = this.rowIndexMapper.getVisualFromRenderableIndex(0);
const visualColumn = this.columnIndexMapper.getVisualFromRenderableIndex(0);
this.selectCell(visualRow, visualColumn);
}
}
# Load data hooks arguments order
Hook afterLoadData has been changed. Its first argument will present a data source that was set during the load data action. Now, a flag informing whether a load of data was done during initialization is the second argument. Also, a new corresponding hook, beforeLoadData, has been introduced, it is called before loading data.
Before:
afterLoadData?: (initialLoad: boolean) => void;
Now:
afterLoadData?: (sourceData: object | void, initialLoad: boolean) => void;
beforeLoadData has the same order of arguments:
beforeLoadData?: (sourceData: object | void, initialLoad: boolean) => void;
# Column and row resizing hooks arguments order
after* and before* hooks related to resizing changed in terms of the order of arguments. Now the first argument is a newSize of a row or column and the second argument is column or row. "Current" prefix was dropped because this hook might not always be called on selection.
Here is the comparison:
Prior 8.0.0:
afterColumnResize?: (currentColumn: number, newSize: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void;
afterRowResize?: (currentRow: number, newSize: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void;
beforeColumnResize?: (currentColumn: number, newSize: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void | number;
beforeRowResize?: (currentRow: number, newSize: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => number | void;
Now:
afterColumnResize?: (newSize: number, column: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void;
afterRowResize?: (newSize: number, row: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void;
beforeColumnResize?: (newSize: number, column: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => void | number;
beforeRowResize?: (newSize: number, row: number, isDoubleClick: boolean) => number | void;
# Selection range have negative indexes
From v8.0.0 selecting columns or rows with headers will include headers as a part of the selection range. We see headers as positioned relatively to the dataset. If the beggining of the dataset is at possition (0, 0) then headers will always have negative indexes. That makes them distingushable from the dataset and they can be easily filtered out if not needed.
When the selection is returned as an array, just map the values and limit them to positive values:
hotInstance.getSelectedLast().map((indexIncludingHeader) => {
return Math.max(0, indexIncludingHeader);
});
Selection Range object has a new method normalize that will do this for you:
hotInstance.getSelectedRangeLast().from.clone().normalize()
# Removals
Hook skipLengthCache was removed because indexMapper is now responsible for the cache and length.
Public methods colOffset and rowOffset were removed and their functionality is now for internal use only.
Also, an experimental feature: ganttChart plugin was removed and is no longer supported.
If you use these features in your project and need backward compatibility, please contact the support (at support@handsontable.com) for further information.



